Are your students struggling to understand multiplication? Teaching with multiplication models can transform how they grasp multiplication facts. When you use these models, it turns memorization into meaningful learning!

These multiplication models will enhance your students’ understanding so they can memorize multiplication facts faster.
Because of multiplication models, students are seeing for the first time that a number in an equation can mean more than just the number of objects. It can mean a unit or a group. They are also seeing that multiplication is a way to represent a repeated addition equation.
When students build this meaning behind multiplication, it helps them commit facts to memory better. They no longer are just memorizing random numbers that go together. They are memorizing with meaning as they think about how many are in each group and how many groups there are. Multiplication models help them visualize multiplication facts.
So what are the models for multiplication?
In this blog post, I’ll be sharing 4 essential models that you should be using to introduce multiplication facts in 3rd grade. Students learn these best when paired with multiplication fact word problems. So let’s get into the 4 models.
Multiplication Set Model
I love starting with multiplication set models because they really help students see that multiplication represents a number of groups and how many are in each group.
To introduce this model, I share a multiplication word problem like this: There are 4 tables in the classroom. 5 students sit at each table. How many students are there in total?
I show how we can represent this model by drawing 4 circles for the tables, and filling in 5 dots in each circle to represent the students. Then we write a repeated addition equation: 5+5+5+5=20. I ask students how many groups we have and how many in each group. So I write, “4 groups of 5.” Then I show the multiplication equation 4X5=20. The first number represents how many groups, the second number represents how many in each group, and the answer shows the total number of objects.
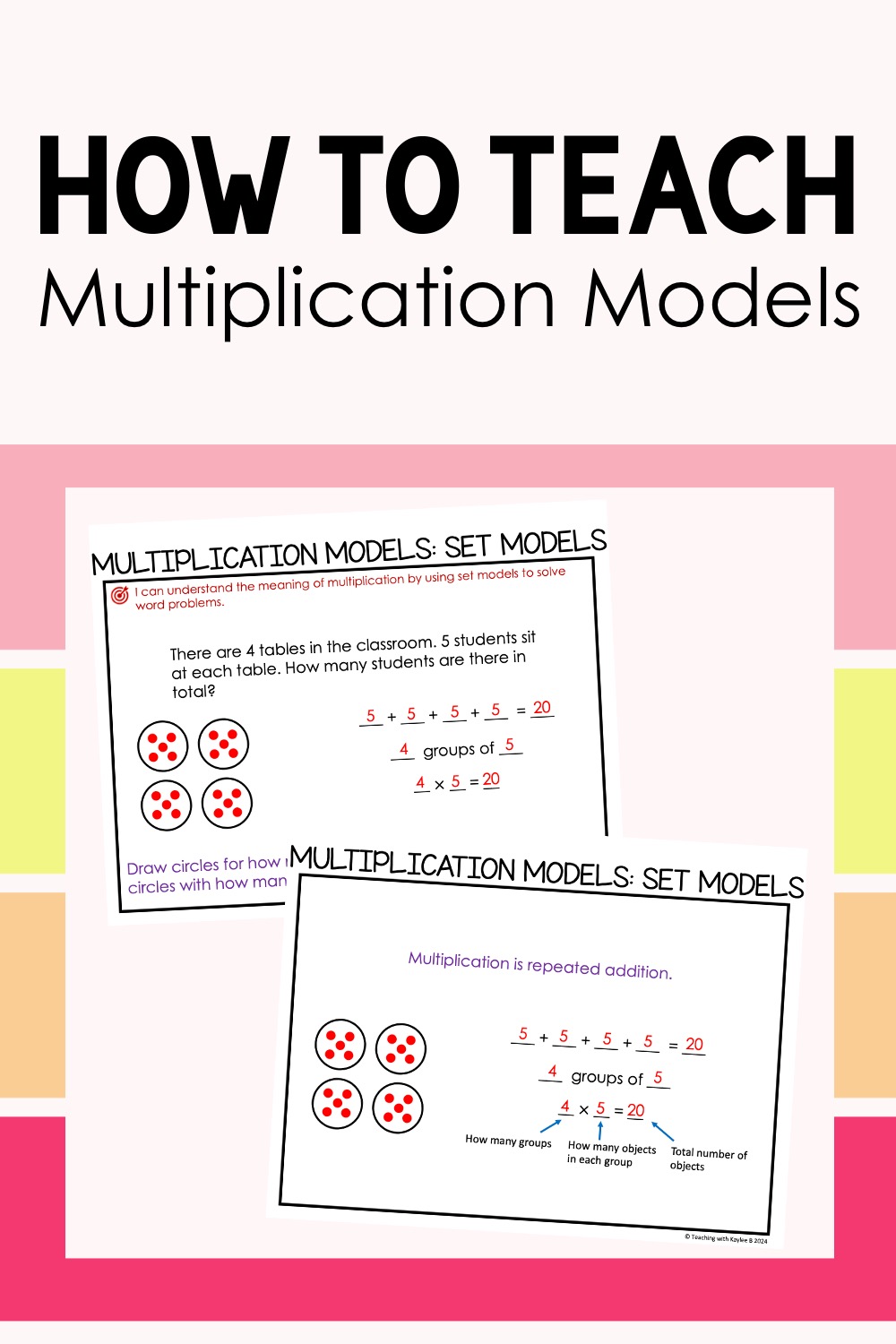
Use models for multiplication to teach the meaning behind multiplication facts.
We practice with another word problem. We draw out the multiplication set model, write the repeated addition equation, and write the multiplication equation.
I love using display pages to teach new concepts. These are like slides that I project up on the board. They make the lesson very visual and guide me on what to say. Find the display pages I use to introduce multiplication here.
Then it’s important to give students guided practice. I like to do this with a worksheet. It follows the same format of the display page examples. Students draw the set model to match the word problems. Then they write the repeated addition equation and the multiplication equation. When students are doing this, it’s good to walk around and monitor how they are doing. Help students where needed and take note of common mistakes and misconceptions. Then you can call students’ attention back and address those things.
For independent practice, you can give students another worksheet. This time they complete it on their own. When my students are doing independent practice, I like to sit over at our classroom table. When students finish their work, they line up by me. I look over their work and help them fix any mistakes.
Then they are ready for some more engaging practice. I give students a partner and they do a fun scoot activity. There are set model task cards taped up around the room. Students take a recording page to each problem and write the multiplication equation that represents the set model shown. Students love getting up and moving with this activity!
Then with that same partner, I have them do a set model puzzle activity. Students match up word problems with its set model and equation. They love the hands-on aspect of this activity.
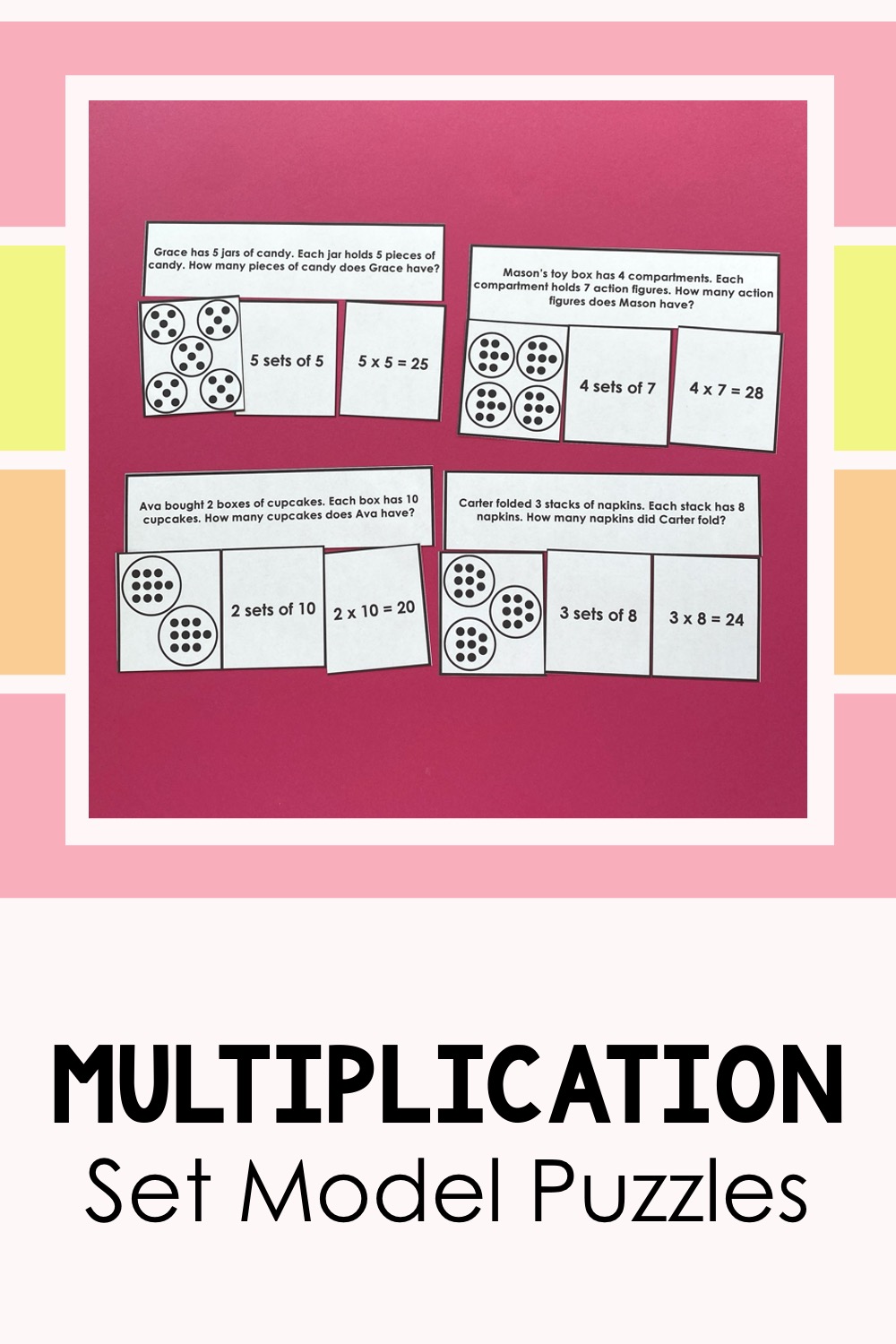
Hands-on learning makes multiplication click! These multiplication set model puzzles help students visually understand groups and totals while building fluency. Perfect for math centers or partner practice!
After students finish that, it’s good to check their understanding. You can have them do an exit ticket where they rate themselves on how they understood the lesson and have them solve a couple set model problems. It’s good to look at these after school and take note of students who could use some extra practice during centers.
For a center activity, I like to laminate set model task cards where students can draw the set models and figure out the answer to the multiplication equation. Students love using dry-erase markers on this activity! This is also a great activity for students who are still struggling with multiplication facts in the middle of the school year. Bring things back to the basics with multiplication models.

Students practice multiplication using models with these interactive task cards! Using dry-erase markers, they draw set models to visualize groups and totals. This makes multiplication more meaningful and engaging.
Ready to make multiplication easier for your students? Grab my Multiplication Set Model Activities to help your students master this strategy with ease here!
But remember, set models are not the only way to represent multiplication. It’s also important to teach multiplication area models.
Multiplication Area Models
An area model represents a multiplication problem using rows and columns of squares within a larger grid. Each row and column helps show how the numbers multiply to find the total.

Multiplication area models are a great way to introduce multiplication with meaning.
Students use repeated addition as they add up either the rows or the columns to find the answer.
I introduce these the same way I did with set models by using display pages. We practice making area models with word problems. Then I get students more practice with multiplication using area models worksheets, a scoot activity, and a puzzle activity.
For the scoot activity, I tape up different area models around the room. Students take their recording sheet and write down the multiplication equation that matches the area model.
Then they do the puzzle activity. Students match up the area model, with its equation and answer.
After that it’s good to check students’ understanding with an exit ticket. Look at these after school to know which students could use more practice with multiplication area models.
Then for centers, you can have them use dry-erase markers on task cards where they draw the area model to represent the equation. Then they add up the rows or the columns to get their answer. Find all of my area model learning materials here.
Area models are similar to arrays, which is another important multiplication model to teach students.
Array Multiplication Models
Arrays are where you arrange objects into rows and columns. Each row has the same number of objects. And each column has the same number of objects. Since they have equal groups, we can use multiplication to represent them and quickly find the total number of objects.

Students model multiplication with arrays by organizing objects into equal rows and columns. This hands-on strategy helps them see multiplication as repeated addition, building a strong foundation for fluency!
Students work with arrays in 2nd grade, so they should look familiar to 3rd grade students.
For arrays, I like to use word problems about rows and columns. Students take the information from the word problem to draw the arrays. From there they write repeated addition equations by looking at the rows and looking at the columns. Students will discover that either way of writing the equation will get them the same answer. It’s a great way to introduce the commutative property of multiplication.
I also have students write the multiplication equations that match their repeated addition equations. I love how easy it is to teach arrays by using display pages. Find the ones I use here.
Learn more about how I teach arrays in 2nd grade in this blog post here.
After teaching arrays, it’s time to get students their own practice. I follow the same format as set models and area models by using worksheets, scoot activities, and puzzle activities.
For the scoot activity, students go around to the different task cards taped up around the room. These task cards have a picture of an array. Students write the multiplication equation to match it.
Then they do the puzzle activity. Students match the array with this repeated addition equation and its multiplication equation. I love how this puzzle activity reinforces the idea that multiplication is repeated addition.
Then it’s good to give students an exit ticket to check their understanding. For centers, you can give students who need more practice task cards where they draw arrays with dry-erase markers.
Find all of my array learning materials here.
And this brings us to our final multiplication model, number line models.
Number Line Multiplication Models
Number line models are where students make equal jumps on a number line to find their answer to a multiplication equation. I think these ones are really great because it helps students find the answer to multiplication equations really quickly. The number lines have numbers on it! So when students land on their final number, that’s their answer!

The number line multiplication model is a great one to build meaning behind multiplication and to help students quickly find the answers to multiplication facts.
I introduce this model the same way as the rest. I use display pages where we work with word problems to draw the model. We make equal jumps on the number line until we land on our answer.
I get students more practice with worksheets, scoot activities and puzzle activities.
For the scoot activity, students go around to the different task cards taped up around the classroom. They look at the number line and how many jumps were made. Also, they look at how many are in each jump. This helps them get the first 2 numbers for their multiplication equation. For the answer, they can look at where the last jump ends.
For the puzzle activity, students match the number line model with its multiplication equation, and answer. Students love finding a place on the floor to solve these puzzles. It’s something different and fun because they don’t have to sit at a desk!
Find all of my number line multiplication model learning resources here.
And those are the 4 essential multiplication models to teach at the beginning of 3rd grade. You can also teach them at the end of 2nd grade as a way to gear students up for 3rd grade math. They are also good to come back to if you have a student who is still really struggling with their multiplication facts in the middle of the school year.
Why do multiplication models help students memorize multiplication facts?
They build meaning behind multiplication. It’s easier to memorize something when you understand the meaning behind it. Also, when students discover something for themselves, they are more likely to commit it to memory. When students use multiplication models, they are discovering the answer for themselves. They will want to commit it to memory rather than drawing out the pictures for an equation over and over again.
I hope you have found this blog post helpful as you introduce multiplication to your students.

Instead of just having students practice with models multiplication worksheets, get them hands-on practice with these interactive task cards!
Want an all-in-one resource for teaching multiplication models? Check out my Multiplication Models Bundle to save time and engage your students!
Students do best with these models when they are fluent with their addition and subtraction math facts. Learn about the strategies I use to teach addition and subtraction facts in this blog post here.


